BUSINESS RESPONSIBILITY REPORT
SECTION A: GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE COMPANY
State Bank of India (SBI) is the nation's largest and oldest bank with a network of 15869 branches. Nearly 10,000 of the 15,869 branches are located in rural and semi urban areas. SBI is the leader in agricultural finance. SBI and its 5 Associate Bank shave more than 48,000 ATM's making it the one of the largest ATM networks in the world. The Bank's ATMs are located in all parts of the country including some of the remotest and inaccessible parts.
The Bank's activities are covered under "Group K: Financial and Insurance Activities of National Industrial Classification (All Economic Activities) - 2008" published by Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. The Bank's activities fall under the below mentioned industrial activity code:
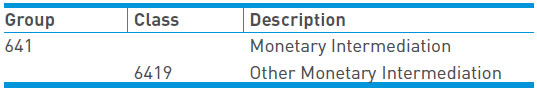
Other financial services like insurance, mutual fund, financial leasing, card business etc. are offered through the Bank's associates and/or subsidiaries to all customer segments whether Government, Corporates or Individuals. The Bank's three major products/services categories, each of which individually comprises of several products/ services, are:
1. Deposits
2. Loans and Advances
3. Remittances and Collections
The Bank's domestic operations are carried out through 14 Circles and 85 Zonal Offices that are located in major cities throughout the country. The International banking services offers a full range of cross border finance solutions for the benefit of its Indian customers, non-resident Indians, foreign entities and banks. With presence across all time zones, State Bank of India and its affiliate banks provide 360 degree services to its global clientele. The International Banking Network is spread across 36 countries with 190 offices. Some of the Bank's International locations include UK, USA, Germany, France, Canada, Russia, South Africa, China, Singapore, Japan and Australia.
The Bank maintains correspondent banking arrangements with 385 reputed international Banks spread over 113 countries. Bank's Joint Ventures and Subsidiaries abroad further underline the Bank's international presence.
Other details about the Bank:

SECTION B: FINANCIAL DETAILS OF THE COMPANY
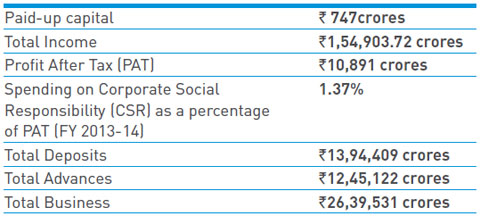
Details for Financial Year 2013-14:
Corporate Social Responsibility has always been a part of the State Bank of India covering various social, environmental and welfare activities. This is rooted in the Bank's belief that it owes a solemn duty to the less fortunate and underprivileged members of the society to make a sustainable social change in their development. In fact since 1973 the Bank is actively involved in nonprofit activity called Community Services Banking. All its branches and administrative offices throughout the country sponsor and participate in large number of welfare activities and social causes.
The budget for the Bank's Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) spending for FY 2013-14 was 1% of the previous year's PAT which amounts to ` 141 crores. The Bank's actual spend on CSR activities for FY 2013-14 was `148.93 crores. The Bank's CSR activities touch the lives of millions of the poor and needy across the length and breadth of the country.
While CSR is embedded in many of the Bank's business initiatives it covers various social, environmental and welfare activities. The Bank has a comprehensive Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Policy, approved by the Executive Committee of the Central Board in August 2011.
The focus areas of the Bank's CSR activities are listed hereunder:
Supporting education.
Supporting healthcare.
Assistance to poor & underprivileged.
Environment protection.
Entrepreneur development programme.
Help in National calamities.
Further details of the Bank's CSR activities have been covered in the "Corporate Social Responsibility" section of the Annual Report 2013-14.
SECTION C: OTHER DETAILS
Participation of subsidiaries and business partners in BR initiatives:
The details of the subsidiaries and joint ventures are provided in the Bank's Annual Report for FY 2013-14.
The Bank's Associates and Subsidiaries fully endorse the BR Principles. However, with their own independent Boards they decide on their own regarding their social and environmental initiatives. Banking operations do not have a complex supply chain and thus the business partners (suppliers/distributors) are also quite limited, which leaves very little scope for the Bank to engage them in its BR initiatives. The Bank expects and encourages its suppliers/distributors to conduct their business in a responsible manner.
SECTION D: BUSINESS RESPONSIBILITY (BR) INFORMATION
Governance related to BR
Director responsible for implementation of the BR policy/policies

Business Responsibility Head

As stated in the Business Responsibility Policy of the Bank, the BR performance of the Bank will be assessed annually by the Board of Directors. The Nodal Officer, heading the BR function, is responsible for the BR performance of the Bank. Further, the Bank's BR Policy will be updated from time to time by the Nodal Officer, in the light of amendments to laws, rules and regulations, as applicable, and an annual review report will be submitted to the Board.
About the BR Report
This is the second Business Responsibility report of the Bank and in accordance with SEBI requirements and published on an annual basis. The BR report for FY 2013-14 can be accessed at Bank's website http://www. sbi.co.in or http://statebankofindia.com under the link Corporate Governance →CSR→BR Report.
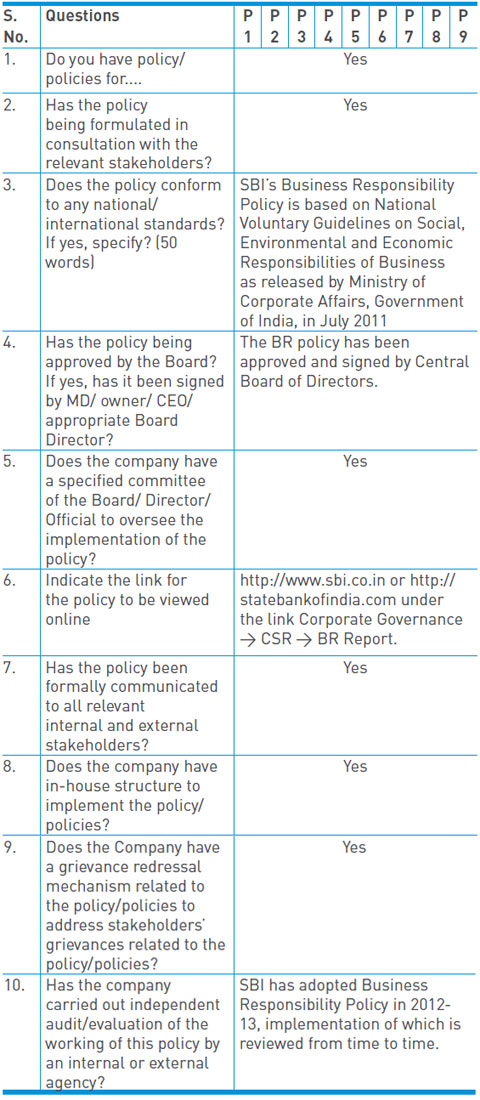
Principle-wise (as per NVGs) BR Policy/policies (Reply in Y/N)
SECTION E: PRINCIPLE-WISE PERFORMANCE
Principle 1: Practicing Good Corporate Governance
The Bank is committed to the best practices in the area of Corporate Governance, in letter and in spirit. The Bank believes that good Corporate Governance is much more than complying with legal and regulatory requirements. Good governance facilitates effective management and control of business, enables the Bank to maintain a high level of business ethics and to optimise the value for all its stakeholders.
The objectives can be summarised as:
To protect and enhance shareholder's value.
To protect the interest of all other stakeholders such as customers, employees and society at large.
To ensure transparency and integrity in communication and to make available full, accurate and clear information to all concerned.
To ensure accountability for performance and customer service and to achieve excellence at all levels.
To provide corporate leadership of highest standard for others to emulate.
The Bank has laid down a well-defined Code of Conduct for its Directors on the Central Board and its Core Management. This Code of Conduct attempts to set forth the guiding principles on which the Bank operates and conducts its daily business with its multitudinous stakeholders, government and regulatory agencies, media, and anyone else with whom it is connected. To get further details, the Code can be easily accessed at the Bank's website. The Bank's Business Responsibility Policy also covers aspects related to ethics, bribery and corruption.
Principle 2: Providing Sustainable Products and Services
As a sustainable business practice,the Bank has consistently delivered products, services and social, environmental and financial returns to support the real economy. For decades it has practiced responsible banking and a consistent commitment to productive economic activity. The Bank has always been at the forefront of innovation whether beits products or its operations/services. SBI has also been a front runner in Technology Innovation/ Absorption.
Some of the recent technology upgrades adopted by the Bank are:
To encourage the growth of e-Commerce, State Bank of India has launched "SBIePay", a payment aggregator services, which facilitates e-Commerce/ m-Commerce transactions between merchants, customers and various financial institutions for all kinds of payments.
SBI through Cash Management Product (CMP) Centre was the first Bank to use NPCI Aadhar Payment Bridge System (APBS) for transferring LPG subsidy based on Aadhar Number.
The Bank has launched an Online Savings Bank Application facility and e-RD, TDR/STDR accounts which evoked enthusiastic response from the customers. Issuance of TDR/STDR through ATMs has been operationalised.
Centralised printing and mailing of current account/ OD/Cash credit statements, housing loan interest certificates, deposit accounts' certificates to enhance customer convenience, were initiated during the reporting period.
The Bank issued a series of new plastic cards for the convenience of their target groups, e.g State Bank Business debit card for corporate customers in two variants-Pride & Premium, Insta Deposit cards enabling traders & service providers to deposit cash quickly, State Bank Virtual Card for retail customers.
State Bank MobiCash Easy, a mobile wallet, was introduced during the year.
E-challan cum return for collection of Employees Provident Fund through Branches and Corporate Internet Banking Channel (CINB).
State Bank Virtual Card enables secured e-commerce on-line transactions, through Internet Banking facility.
Green Channel Counter, Self Service Kiosk, Green Remit Card, prepaid cards like Smart Payout card, Ez Pay Card, Vishwa Yatra Card are some of the initiatives of the Bank's green initiatives and have social benefits also.
Principle 3: Caring for Human Capital
Employee Strength
The Bank is one of the largest employers in the country having 2,22,033 employees at the end of FY 2013-14, of which 2,610 persons with disabilities. As on 31st March 2014, the Bank had 42,744 Schedule Caste and 17,243 Schedule Tribe employees.
Employee Benefits
The vision of the Bank for its human resources is to create an enabling environment to enhance the efficiency of the organisation. The aim is to encourage the employees to perform to their best ability by a system of proper placements, incentives, while creating an atmosphere of trust and a feeling that the organisation cares about the well-being and personal aspirations of the staff. This helps align personal aspirations with professional goals and help enhance efficiency. The Bank runs multiple benefit schemes for its employees some of which include providing them provident fund, gratuity, pension, medical benefits, concessionary interest rates on advances, higher interest rates on deposits, scholarships to employees' children, holiday homes, reservation in schools, grant of sabbatical leave to employees, executive health check-up etc.
Freedom of Association
The Bank has two recognised Employee Associations – One for Supervising Staff and the other for Award Staff. The names of the associations are:
1 All India State Bank of India Officer's Federation.
2. State Bank of India Staff Federation
The majority of staff and officers are members of these federations.
Human Rights
Recruitment policy of the Bank does not permit any engagement of child labour, forced labour or involuntary labour. An independent complaint committee have been constituted at, Local Head Offices (LHOs), Administrative offices and Regional Business offices (RBOs) level & a Contact Coordinator at Corporate Centre to handle complaints of sexual harassment at work place, promptly and appropriately. The Bank refrains from any discrimination on the basis of caste, creed, gender or religion and strives to ensure a healthy work-life balance for its employees.
Employee Training & Development
The Bank has a very elaborate training network comprising of 47 Learning Centres and 5 Apex Institutes developed over 50 years to cater to the competence building. The Bank's training system functions under the overall supervision and guidance of the Strategic Training Unit, headed by a very senior level executive.
The Strategic Training Unit ensures:
All employees to undergo at least one institutional training during a year.
Training programs are aligned with current corporate priorities / requirements of Business Units.
A culture of self-learning is inculcated in every employee.
Active promotion of online learning, including mandatory role-based lessons supported by Rewards & Recognitions.
E-learning has proved to be an effective platform in providing supplementary support to institutional training. Some of the highlights of 2013-14:
More than 2,34,763 participants trained during 2013-14 covering 60% of Officials and 68% of Award Staff.
219 short duration e-capsules (of 15 minutes each) uploaded for faster dissemination of knowledge amongst employees, especially frontline staff.
Mobile nuggets (short study materials on mobile handsets) made available on pilot basis.
All employees are made aware of gender sensitivity at work place.
Senior officials motivated to pursue Harvard Manage Mentor, an online course on management issues under tie up with Harvard Business School.
Video lectures on industry specific inputs arranged for senior executives.
Principle 4: Engaging with Stakeholders
The Bank's approach to stakeholder engagement helps to minimise risks, identify ideas for new products and services, and understand and respond to the issues that matter to the communities it serves.
The Bank communicates with the stakeholders through a variety of channels, such as e-mails, website, conference call, Press Meets, Advertising, one-on-one meeting, analysts' meet and attendance at Investor Conference throughout the world. Stakeholder engagement is embedded in all areas of the Bank. The Bank seeks feedback through all their customer-facing channels, listens to all shareholders concerns and provides opportunities for employees to provide feedback. The engagement with stakeholders is through social media like Facebook & twitter, and active participation in a variety of industry and community associations.
Principle 5: Respecting Human Rights
The Bank recognises its responsibility to respect human rights within its sphere of influence which it defines as:
Employees
Suppliers and Service Providers
Retail clients and corporate clients
Local communities
The bank has a direct obligation to protect the human rights of its employees, including the right to equal opportunities, protection from discrimination and fair working conditions. The Bank does not use child labour or forced labour among its own staff. The Bank seeks to ensure that their principal suppliers respect human rights and that its corporate clients comply with all the regulations in regard to human rights. SBI makes a positive contribution to local communities through its various CSR and microfinance activities.
Principle 6: Caring for Environment
The Bank takes proactive steps to reduce the direct impact of its operations on the environment. From recycling programs to energy conservation in offices and branches, the Bank is working to reduce its operational footprints on the environment. Some of the measures introduced are:
Wind based power projects have been successfully commissioned and the power generated from these projects helps power Bank's branches/offices in the States of Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
Installation of Solar ATMs, introduction of Green Channel Banking (Paperless Banking).
The Bank has initiated a pilot project to determine its Carbon footprint levels, which will help in determining the Bank's resource consumption pattern and enable the Bank to take effective steps to implement various measures for sustainable usage in a cost effective way.
The Bank has put in place SMART i.e. Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time bound Green Banking Goals, some of which are obtaining star rating at all Local Head Offices premises from Bureau of Energy Efficiency, construction of 'Green' buildings, waste water treatment, programs to sensitise staff on energy savings.
Our over 48,000 ATM's ensures reduced consumption of paper at Branches.
The Bank's operations generate very minimal emissions/ waste and hence, the quantity of emissions/wastes generated by the Bank in the reporting period was far below the permissible limits given by the Pollution Control Board. The Bank didn't receive any show cause/legal notice by Pollution Control Board during the FY 2013-14.
Principle 7: Advocating Public Policy
The Bank's participation in public policy making process is multi-layered. At the leadership level, the Top Management meets regularly with Policy makers and regulatory authorities. At the policy development level, top executives meet with regulators, governments and government agencies on public policy issues relevant to the financial services industry. This engagement takes a number of forms, including participation in government advisory bodies.
The Bank has been an active member of various banking and finance-related Trade bodies, Chambers and Associations. Some of the major associations which SBI is a part of are listed hereunder:
Indian Bank's Association (IBA),
Foreign Exchange Dealers Association of India (FEDAI),
Fixed Income Money Market and Derivatives Association (FIMMDA),
The Bank is also associated with ASSOCHAM, CII etc.
The Bank's advocacy of policy has been for the overall benefit to the Society, and does not serve any sectarian interest.
Principle 8: Enabling Inclusive Growth
To achieve the twin objectives of ensuring greater financial inclusion and increasing the outreach of the Bank and to provide comprehensive financial services to the underprivileged especially in unbanked areas the Bank's scheme for Financial Inclusion includes extending Banking services through Business Correspondents (BCs).
The Bank has set up 45,487 BC Customer Service Points through alliances both at national and regional level.
The Bank is offering various technological enabled products through Business Correspondent (BC) channel, such as, Savings Bank, flexi RD, STDR, remittance & SB-OD facilities.
The Bank has achieved 100% coverage under financial inclusion in 31,729 villages during FY 2013-14. The cumulative coverage of villages has gone up to 52,260.
11,423 BC outlets have been set up in Urban/Metro centers which cater to the requirements of migrant labourers, vendors, etc. During FY 2013-14, 226 lakhs remittance transactions for ` 9,983 crores were registered through BC channel.
During FY 2013-14, Bank has opened 1.50 crores Small accounts with simplified KYC and this taking overall tally to 3.53 crores accounts.
The transactions volume through BC Channel has grown to ` 22,525 crores during FY 2013- 14 as against ` 13,033 crores during FY 2012-13.
With a view to facilitate transactions through alternate channels, the Bank has issued 24 lakhs FI Rupay ATM Debit Cards to FI customers.
Linking of villages to branches through CSPs in a hub and spoke model has been launched and 69,749 villages have been linked so far. A facility of depositing loan repayments at 31,919 BC outlets has also been enabled.
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Scheme has been successfully rolled out.
The Bank has successfully completed 27.41 lakhs transactions amounting to ` 505 crores as Sponsoring Bank in addition to handling 7.1 lakhs transactions amounting to ` 98.61 crores as Receiving Bank. Overall 1.36 crores accounts linked with Aadhaar across the country.
SBI is the sole Sponsoring Bank for DBT for LPG transactions which are processed centrally for all the three Oil Marketing Companies. Over 8.98 crores transactions amounting ` 5,393 crores successfully processed.
4.46 lakhs SHGs credit linked with credit deployment of ` 5,134 crores. Our market share in SHGs is 22%.
The Bank has spent a total amount of ` 148.93 crores on CSR activities in FY 2013-14. The details of the activities and projects undertaken have been covered above in Section B as well as in "Corporate Social Responsibility" section of the Annual Report.
Principle 9: Serving Customers
The Bank's vision statement clearly spells out the centricity of the customer in the Bank's business strategies and operations. A multi-tiered structure of committees constantly review existing services and suggest improvements. Important issues raised by these Committees and action taken thereon, as well as analysis of the consolidated data for customer grievances for all Circles are placed before the Customer Service Committee of the Board every quarter, to identify common systemic and policy issues that require rectification.
The Bank has a well-defined and documented Grievance Redressal Policy which provides for:
A dedicated Customer Care Cell.
Bank's Web based Complaint Management System (CMS) has been redesigned and launched as a single online Grievance Lodging and Redressal System for the Bank. Customers can lodge their complaints either through various channels including written complaint at branch or by calling at the toll free number of Bank's Contact Centre or sending SMS message 'UNHAPPY' to a specified number.
Process innovations
Relationship management platform was strengthened across business verticals, which included accounts management teams for corporate customers, premier banking services for high net worth customers, relationship managers for SMEs (ME&SE).
The number of processing cells (RACPCs/ SMECCs), supported by loan origination software, were increased and revamped, for quicker processing of loans.
Touch-points with customers were expanded, through opening of branches and increasing.
Customer Service Points, BC outlets in remote area.
Cluster models were introduced at all currency chest branches for efficient cash management at semi-urban/ rural area.




